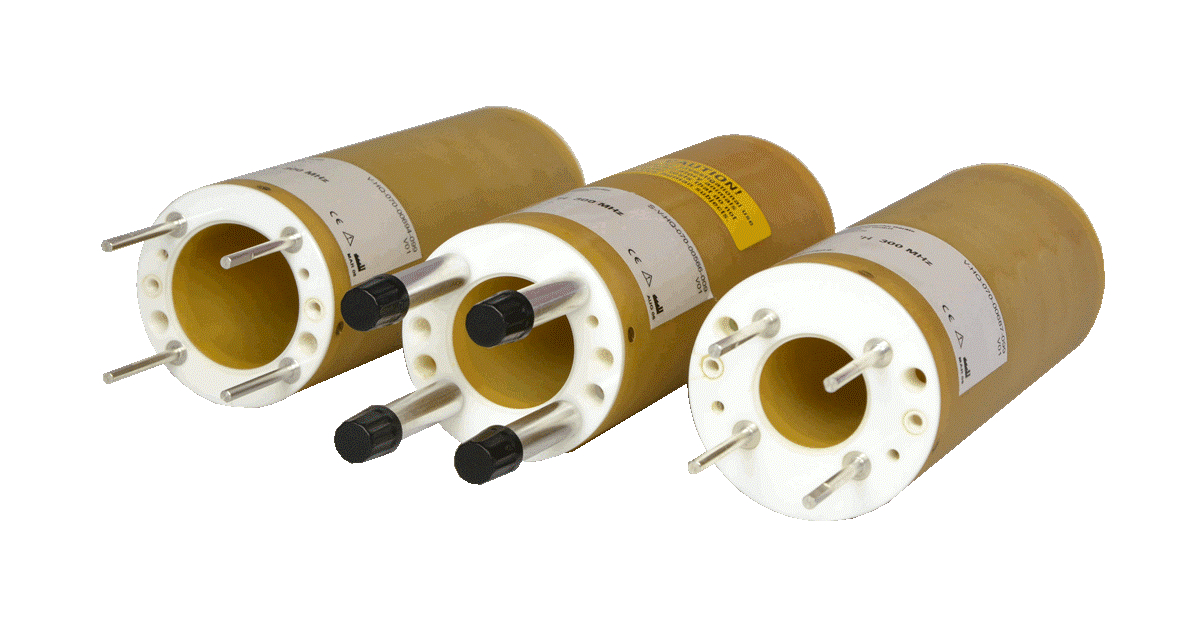
Mouse Head Volume Coils
Description
▪ homogeneous RF profile over the mouse head
▪ quadrature polarization, transmit / receive
▪ inner diameters from 20 to 40 mm, other on demand
▪ multi nuclei versions available
Individually adaptable to the established systems like Bruker, Agilent, Varian and clinical scanners at any field strength.
Please contact us for availability on your NMR system.
No Medical Device! Caution – The use of the devices described above is limited to investigational use on laboratory animals or other tests that do not involve human subjects.
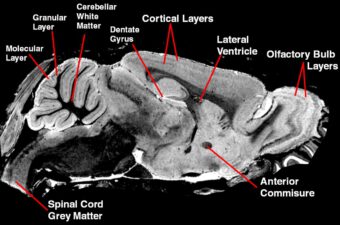
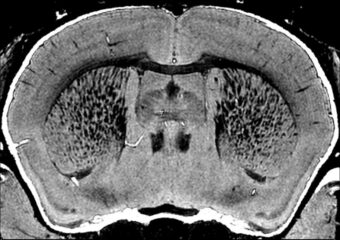
Transmit / receive volume coil for mouse head at 9.4 T
Image courtesy: Jon Cleary, University College London, U.K.
Datasheet
Publications
S. Koch et al.: Atlas registration for edema-corrected MRI lesion volume in mouse stroke models.
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 0(00) 1–11 (2017)
with RAPID Biomedical transmit/receive volume coil (17/59 mm) # V-HQ-070-00521-001
P. Boehm-Sturm et al.: Neuroimaging Biomarkers Predict Brain Structural Connectivity Change in a Mouse Model of Vascular Cognitive Impairment.
Stroke, 48:468-475. DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.014394. (2017)
with RAPID Biomedical transmit/receive volume coil (20/112 mm)
# V-HQ-070-01708-001 V01
A.Z. Caron et al.: The SIRT1 deacetylase protects mice against the symptoms of metabolic syndrome.
The FASEB Journal, Vol.28/No.3 , pp:1306-1316, doi: 10.1096/fj.13-243568 (November 2016)
with RAPID Biomedical transmit volume coil # V-HQS-070-01332-001 V01
E.G. Hain et al.: Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in the Mouse Is Associated with Decrease of Viscoelasticity of Substantia Nigra Tissue.
PLOS ONE | DOI:10.1371 /journal.pone.0161179 (August 15, 2016)
with RAPID Biomedical transmit/receive volume coil (17/59 mm) # V-HQ-070-00521-001
S. Donath et al.: Interaction of ARC and Daxx: A Novel Endogenous Target to Preserve Motor Function and Cell Loss after Focal Brain Ischemia in Mice.
The Journal of Neuroscience, 8132 • 36(31), 8132– 8148 (August 3, 2016)
with RAPID Biomedical transmit/receive volume coil (17/59 mm) # V-HQ-070-00521-001
N.M. Jadayji et al.: Elevated levels of plasma homocysteine, deficiencies in dietary folic acid and uracil–DNA glycosylase impair learning in a mouse model of vascular cognitive impairment.
Elsevier Behavioural Brain Research, 283, pages 215-226 (2015)
with RAPID Biomedical transmit/receive volume coil # V-HQ-070-01708-001 V01
N. Smart et al.: De novo cardiomyocytes from within the activated adult heart after injury.
Nature, doi: 10.1038/nature10188 (2011)
with RAPID Biomedical volume coil for mouse heart # V-HQ-094-00685-001